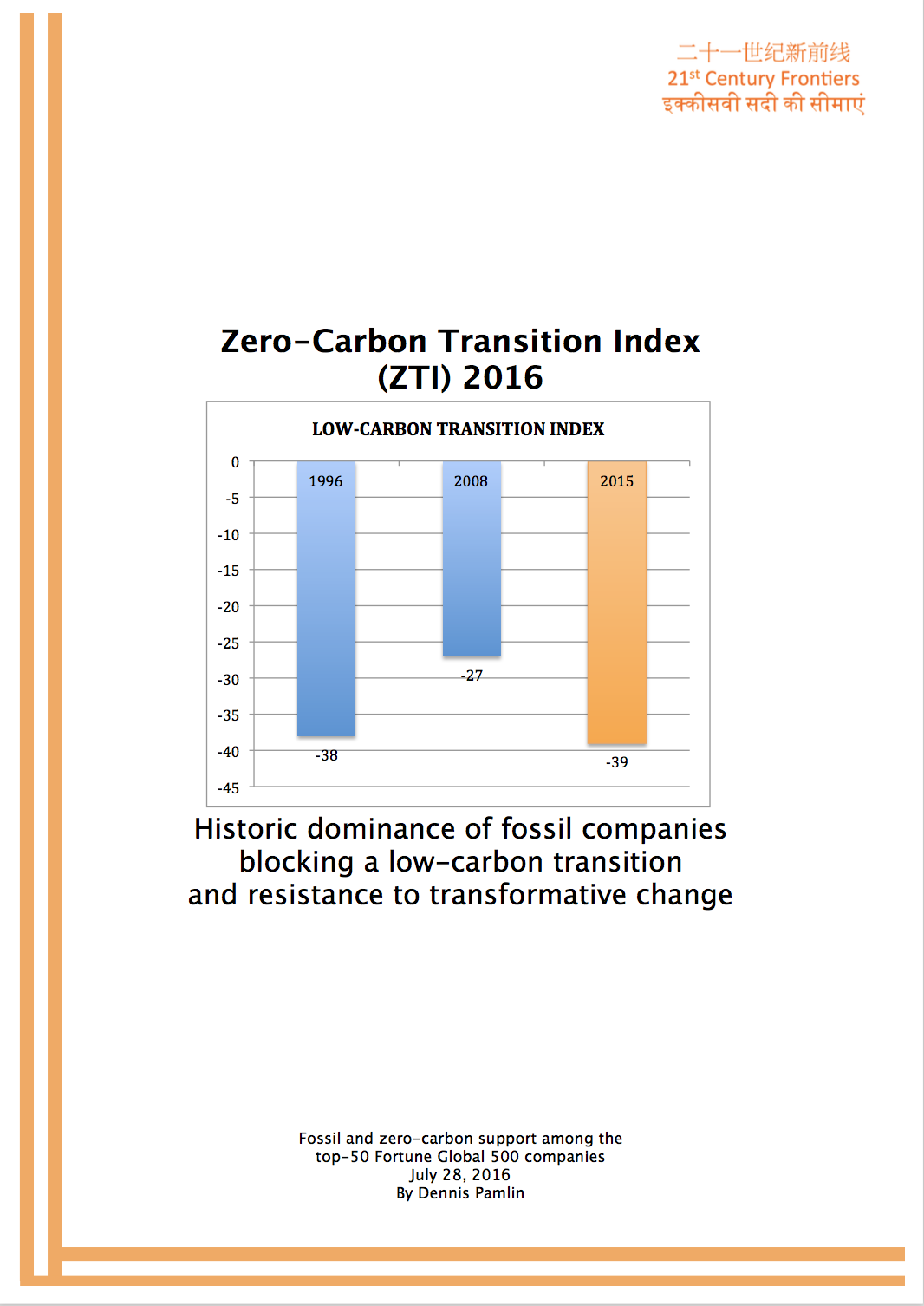
Assessment of Global Low-Carbon and Environmental Leadership in the ICT Sector (Report)
/Role: author with Simon Mingay
Summary
The information and communication technology (ICT) industry and its individual providers are at an important juncture. Are they really going to commit themselves to the necessary investments to develop low-carbon and environmental solutions during a period when, with some exceptions (such as energy-efficient ICT equipment, intelligent buildings and smart grids), the markets for any such solutions are at best emerging? We look at which providers are placing their bets and developing the capabilities that will make them effective innovation partners for enterprises and give them platforms for leadership in a low-carbon and more sustainable economy.
Key Findings
During 2009 and 2010, there has been rapid progress in the maturity of ICT vendors in terms of their internal environmental programs and in terms of the development of a set of low-carbon market offerings. The dominance of talking in 2008 has evolved into a lot more action in 2010 in terms of suitable products, services development and policy- related activity.
We now have a clear group of market makers (BT, IBM, Cisco, Ericsson, HP, Fujitsu and SAP) that we believe are beginning to build distinguishing capabilities.
The 2008 leaders, such as IBM, BT, Ericsson, Fujitsu and HP, have maintained their relatively strong positions with good, well-rounded low-carbon and environmental programs, improving their own internal performance, and developing market-facing solutions ranging from more-energy-efficient ICT equipment and mobile phone networks, through logistics and transportation, to solutions that enable smart grids.
Aside from the important task of making ICT equipment more energy efficient, and a couple of particularly hot areas such as smart grids, developing solutions for a low- carbon economy is definitely not yet "core business."
With a couple of exceptions, the industry is hobbled by the short-term incremental sustainability-related goals that it is setting for itself, rather than setting more- challenging, longer-term goals that could result in transformative solutions.
There are limited signs of disruptive innovation, and more of a focus on incrementalism.
The industry is fearful of committing its weight to influencing national and international climate change and sustainability policy; rather, it is standing on the sidelines as a cheerleader.
© 2010 Gartner, Inc. and/or its Affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of this publication in any form without prior written permission is forbidden. The information contained herein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable. Gartner disclaims all warranties as to the accuracy, completeness or adequacy of such information. Although Gartner's research may discuss legal issues related to the information technology business, Gartner does not provide legal advice or services and its research should not be construed or used as such. Gartner shall have no liability for errors, omissions or inadequacies in the information contained herein or for interpretations thereof. The opinions expressed herein are subject to change without notice.
The industry no longer predominantly sees climate change and sustainability as a risk, but sees it as an emerging opportunity.
Service and software providers have improved their positions from 2008, but remain relatively immature in terms of their internal programs and their market offerings. SAP would stand out as a relatively strong performer with big improvements in its internal programs, transparency, product development and road map.
Management of the environmental performance of the supply chain remains an area of significant differentiation, demanding much higher standards from everyone if the ICT industry is to credibly defend its position as a climate leader.
ICT providers in Asia (not Japan) are still lagging overall, but we have seen some dramatic improvements, and we would anticipate that continuing.
IT organizations still need to pay close attention to the balanced nature of the programs from IT providers, covering all areas of influence from direct, indirect and policy issues. We still see plenty of examples of providers with significant gaps in their programs.
Interindustry partnerships are starting to emerge, particularly from the leaders. For example, IBM and Johnson Controls developing intelligent building solutions. These partnerships are a very significant and important step in the ability of ICTs to develop commercially viable solutions for a low-carbon economy.
While the recent Global e-Sustainability Initiative (GeSI) and Boston Consulting Group (BCG) report outlining a high-level methodology for measuring the enabling effects of ICT related to the climate is a good step forward, the industry has so far only made a limited attempt at measuring the environmental benefits of its solutions, and has made no attempt at all to understand their systemic and rebound impacts. (That is, the indirect and frequently unforeseen change in behaviors, consumption patterns and so on, resulting from the introduction of new technologies, policy measures, etc.)
The industry continues to bask in the afterglow of the Smart 2020 report (www.smart2020.org), when it should really be moving that thinking forward at a much faster pace.